
Medicare Supplement (Medigap) vs Medicare Advantage
Understanding the differences between Medicare Supplement (Medigap) and Medicare Advantage plans is essential when you're enrolling in Medicare. These two options serve different purposes and cater to varying healthcare needs and preferences. Here's a comparison to help you make an informed decision:
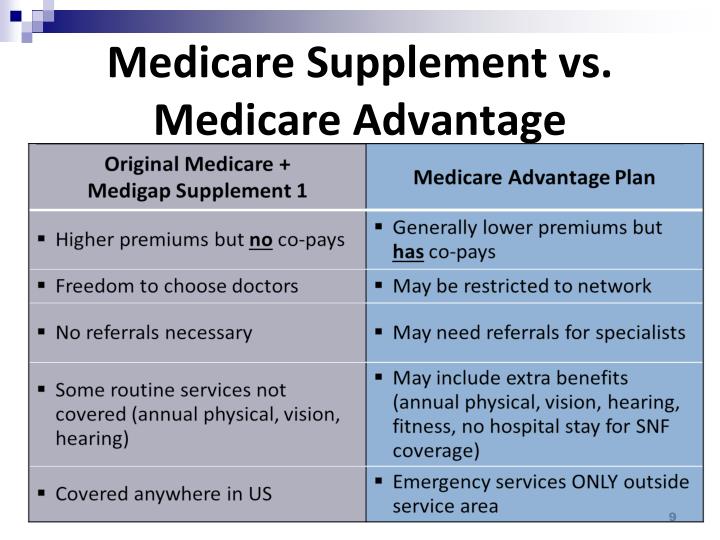
Medicare Supplement (Medigap) Plans:
- Coverage: Medigap plans work alongside Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) and are designed to fill the gaps in coverage. They help pay for out-of-pocket costs such as deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments that Medicare doesn't cover.
- Network: With Medigap plans, you have the flexibility to see any healthcare provider who accepts Medicare. There are no restrictive networks, allowing you to choose your doctors and hospitals without referrals.
- Costs: While Medigap plans typically have higher monthly premiums than Medicare Advantage plans, they offer predictability in healthcare expenses. You won't face unexpected out-of-pocket costs for covered services.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: Medigap plans do not include prescription drug coverage (Part D). You'll need to purchase a standalone Part D plan to cover your medications.
- Additional Benefits: Medigap plans usually do not offer additional benefits like dental, vision, or fitness programs. They focus on core Medicare coverage.
- Portability: You can keep your Medigap plan regardless of where you live in the United States. It's not tied to a specific location.
Medicare Advantage Plans:
- Coverage: Medicare Advantage plans, also known as Medicare Part C, are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. They provide all of the benefits of Original Medicare (Parts A and B) and often include extra benefits like prescription drug coverage, dental, vision, hearing, and fitness programs.
- Network: Most Medicare Advantage plans have provider networks, such as Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) or Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). You may be required to use network providers and get referrals for specialist care in some plans.
- Costs: Medicare Advantage plans typically have lower monthly premiums than Medigap plans but can have higher out-of-pocket costs when you receive care. These costs may include copayments and deductibles for doctor visits and hospital stays.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: Many Medicare Advantage plans include prescription drug coverage (Part D) as part of the plan, offering convenience for those who need medication coverage.
- Additional Benefits: Medicare Advantage plans often offer a range of additional benefits beyond what Original Medicare provides. These can include routine dental, vision, hearing, and wellness programs.
- Portability: Your Medicare Advantage plan may have restrictions if you move out of the plan's service area. In such cases, you may need to choose a new plan.
Choosing Between Medigap and Medicare Advantage:
The choice between Medigap and Medicare Advantage depends on your specific healthcare needs, preferences, and financial considerations. Here are some factors to consider:
- If you want maximum flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and don't mind paying higher monthly premiums, Medigap might be a good choice.
- If you prefer a lower monthly premium and are comfortable with network restrictions, a Medicare Advantage plan could be more affordable.
- If you have specific healthcare needs, such as frequent doctor visits or prescription medications, a Medicare Advantage plan with comprehensive coverage might be a better fit.
- Consider whether additional benefits like dental, vision, and prescription drug coverage are essential to you.
- Think about how much you're willing to pay out of pocket for healthcare services versus having predictable, higher monthly premiums.
Ultimately, the decision between Medigap and Medicare Advantage should align with your healthcare priorities and budget. It's advisable to compare plan options, review their costs and coverage, and consult with a Medicare specialist to make an informed choice.